
Lean Management A SocioTechnical Systems Approach to Change STS Roundtable
Examines sociotechnical systems (STS) theory and presents classical organization theories of Burns and Stalker, Woodward, Perrow, Thompson and Trist to develop a contemporary OD intervention in terms of self‐regulating work groups (self‐leading or self‐managing teams) performing interrelated technological tasks..

The Importance of Sociotechnical Systems Lucidchart Blog
Insights: - The human-centered AI (HCAI) approach and the sociotechnical systems (STS) theory share the same goal: ensuring that new technologies such as AI best serve humans in a sociotechnical environment. - HCAI practice needs to fully embrace sociotechnical systems thinking, while traditional STS needs to evolve to address the emerging characteristics of AI technology. - We propose a.

Hexagonal sociotechnical systems framework (adapted from Clegg 1979;... Download Scientific
Sociotechnical Systems (STS) theory was initially developed by members of the Tavistock Institute in London, with the primary objective to improve the overall quality of working life (for a review, see Mumford ). A sociotechnical system is the synergistic combination of humans, machines, environments, work activities and organisational.

Communication Breakdown & Sociotechnical Systems Theory YouTube
This paper reviews the development of sociotechnical systems theory and research over the past 30 years, paying particular attention to the evolution of the paradigm in North America during the past decade. Elements of sociotechnical systems theory discussed here include the conceptualization of social systems, technical systems, and open.
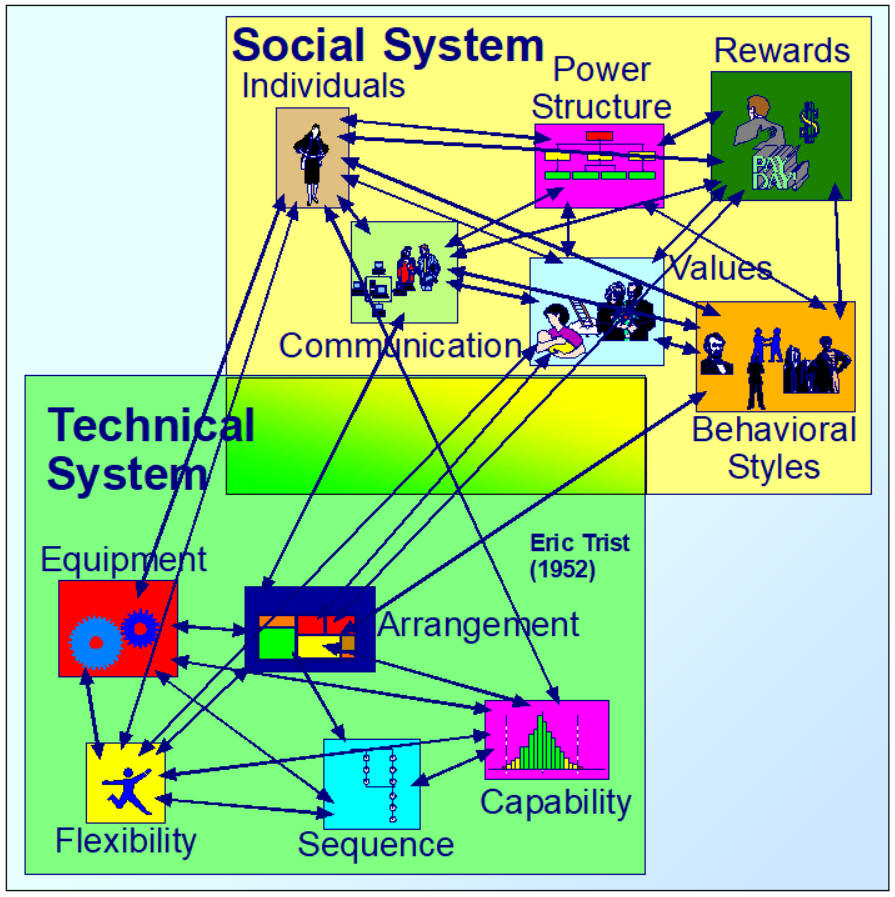
Socio Technical Systems (STS){Strategos}
Sociotechnical systems theory is a mixture of sociotechnical theory, joint optimisation and so forth and general systems theory. The term sociotechnical system recognises that organizations have boundaries and that transactions occur within the system (and its sub-systems) and between the wider context and dynamics of the environment. It is an.
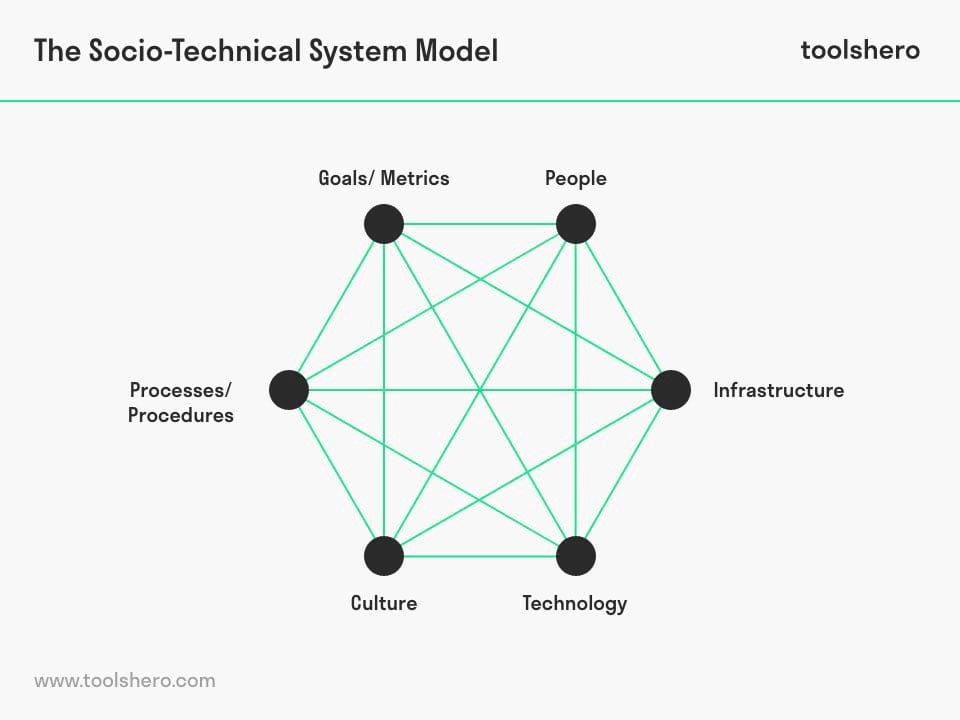
Socio Technical System definition, theory & example Toolshero
Sociotechnical systems theory (STS) is an organizational design approach with a core focus on the interaction between people and technology. Sociotechnical systems theory is based on two main principles. The first is that interaction between social and technical factors creates the conditions necessary for optimal or sub-optimal performance.

Interventions and Actions in a SocioTechnical System (IASTS) model Download Scientific Diagram
The sociotechnical theory. Essentially, sociotechnical systems theory sees the holistic, interconnected contribution of technology and the human systems that operate and interact with it. As people and tech function together, they form a system, one that adds complexity and is more than the "sum of its parts.".

The sociotechnical systems perspective. Download Scientific Diagram
1 Introduction. Socio-technical systems design (STSD) methods are an approach to design that consider human, social and organisational factors, 1 as well as technical factors in the design of organisational systems. They have a long history and are intended to ensure that the technical and organisational aspects of a system are considered together.

A generic model of sociotechnical system levels based on [9]. Download Scientific Diagram
Works with Your Schedule, Tablet or Phone. Start Now! Find Your STS Theory & Characteristics Online with Our Video Lessons.

Sociotechnical Systems Theory Model as Applied to GUSD and Translation... Download Scientific
Since sociotechnical systems are very complex, and do not have owners, the idea of managing or governing sociotechnical systems is often framed as reflexive, evolutionary, and adaptive processes (Smith and Stirling, 2007, Voß et al., 2009), maintaining the objective of developing instrumental models to steer ongoing change (Smith et al., 2010.

Sociotechnical systems theory. Download Scientific Diagram
The theory stipulates that the success of the socio-technical system is a product of the interactions between these subsystems. Socio-technical theory emerged in response to dominant technocratic models that were technologically deterministic, ignoring human factors (Kling, 1980; Trist, 1981).

Sociotechnical systems theory. Download Scientific Diagram
The past. Sociotechnical systems design (STS) as conceived by Trist, Emery and others (Trist & Bamforth, Citation 1951; Trist, Higgin, Murray, & Pollock, Citation 1963) was intended to enhance the performance of work systems by recognizing the ways in which the behaviours of human actors affect the operation of technology.More specifically, better operational performance could be achieved when.

[PDF] Sociotechnical Systems Theory and Environmental Sustainability Semantic Scholar
Socio-technical systems theory is a perspective on the architecture of social organizations that emphasizes the interrelationship of the technical and social dimensions [2], [16] - [19]. The.

Figure 2 from Advancing a sociotechnical systems approach to workplace safety developing the
Socio-technical systems theory. Within the STC we adopt a systems view of organisations, represented by the hexagon. It is this hexagon that lies at the heart of our thinking. Within a socio-technical systems perspective, any organisation, or part of it, is made up of a set of interacting sub-systems, as shown in the diagram below.

Virtual DomainDriven Design A community of practise
Socio-technical systems theory explores how social and technical elements interact. Organizations work best when their social and technological parts align. Socio-technical systems theory believes people and technology should not be separated in analysis. Instead, you should view them as interconnected parts of a whole system.
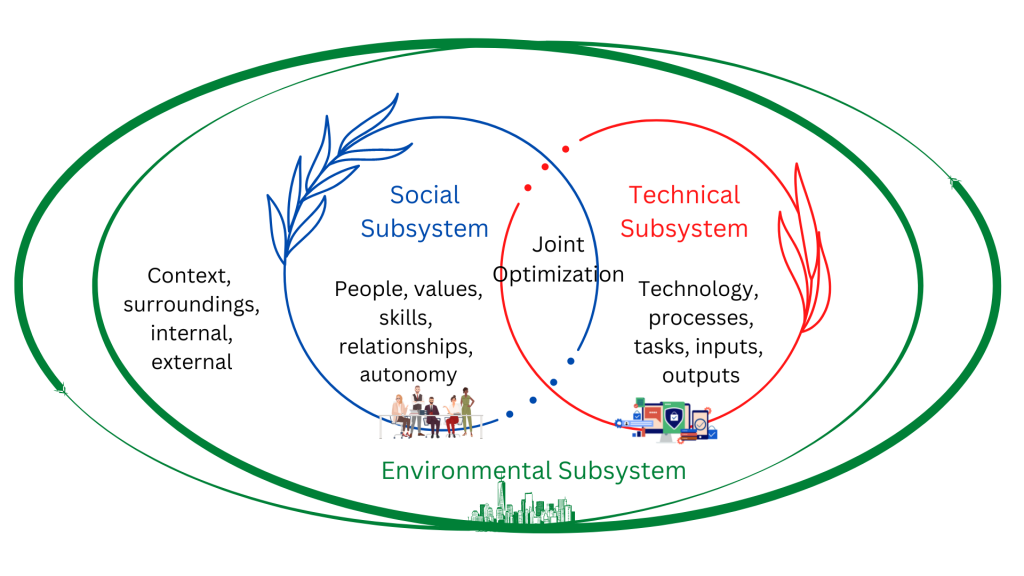
Theory applied to informatics SocioTechnical Theory
Sociotechnical systems theory has traditionally been concerned with work systems in which a number of people have a role to play in a collective task be it coal mining, car assembly or care for the sick. Engagement with a large task leads to division of labour between the people involved and this produces task interdependencies between them; in.